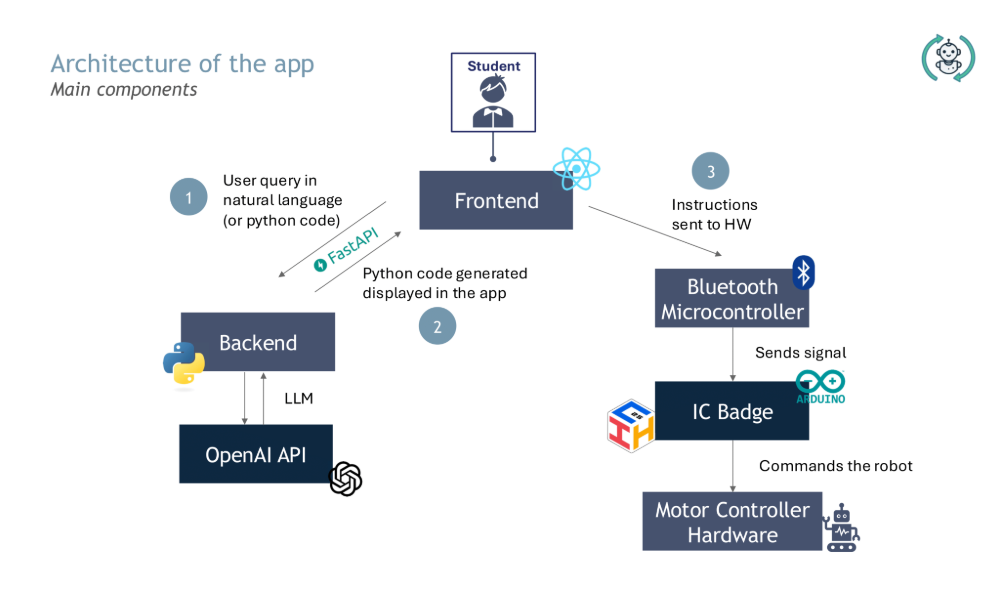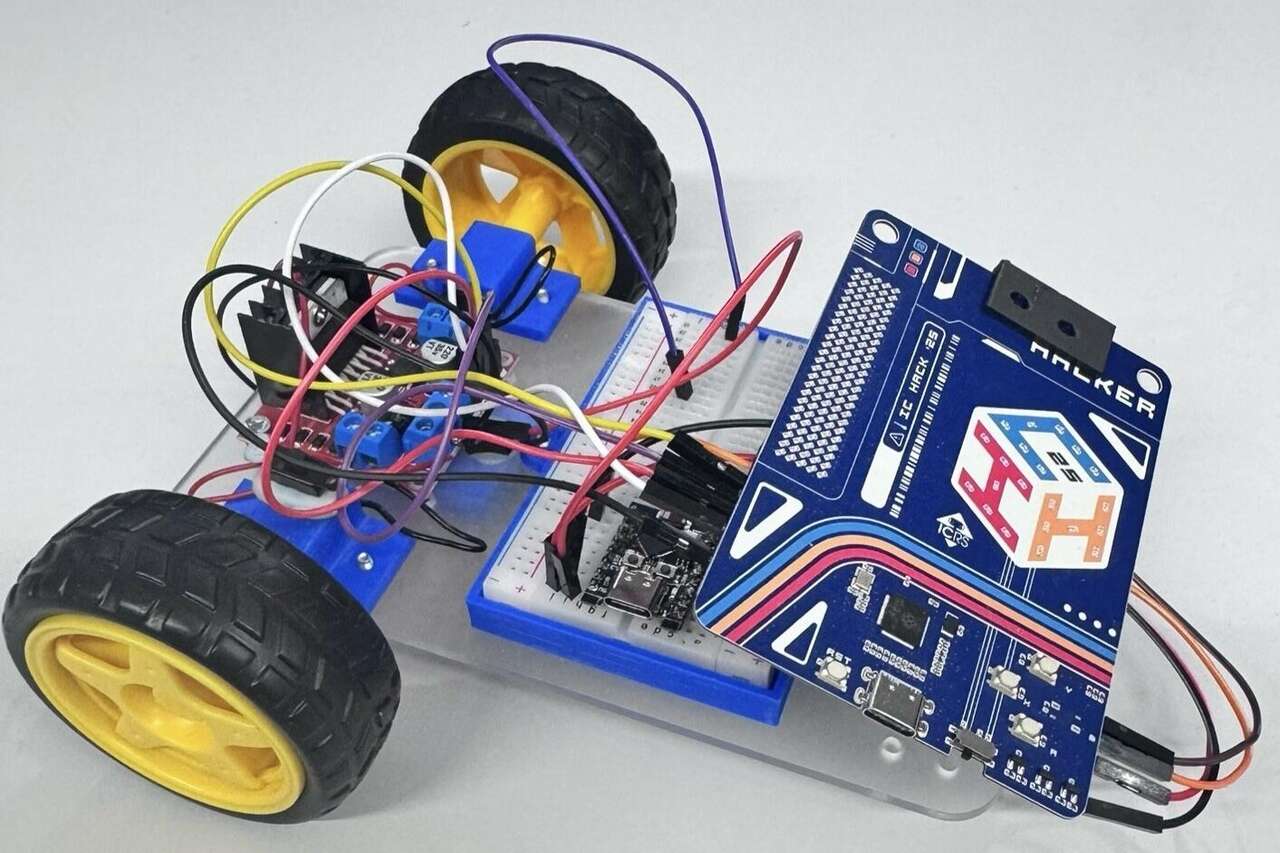
Edu-Rob is a browser-based system that teaches Python by letting users program a robot with natural-language prompts. A constrained LLM (Large Language Model) returns a minimal script using only the allowed movement functions and simple control flow; the frontend extracts those calls and transmits a serialised command list over Web Bluetooth to an ESP32, which bridges to the IC-Badge controller to drive the motors and show the active direction on its LED display.



The UI collects the user’s action list in plain English and submits it to an LLM (Large Language Model) under a strict system prompt. The return must be a single Python script that uses only the whitelisted movement functions and the keywords if, else, for, and while. The frontend validates the script by rejecting disallowed identifiers, imports, I/O, or comments, enforcing simple loop bounds, and checking the expected instruction count. The validated script is then reduced to a canonical sequence of opcodes (for example FORWARDS, RIGHT 90) that matches the teaching examples in the slides.
The opcode sequence is framed into compact messages and streamed over the Web Bluetooth API (Application Programming Interface) to the ESP32. Each message is acknowledged before the next is sent. The ESP32 forwards the commands over UART0 (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) to the ICHACK-Badge interpreter, which drives the motor controller via GPIO (General-Purpose Input/Output)/PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) and updates the badge LED with the active action. The app surfaces acknowledgements and errors so users can see exactly how their prompt maps to movement.